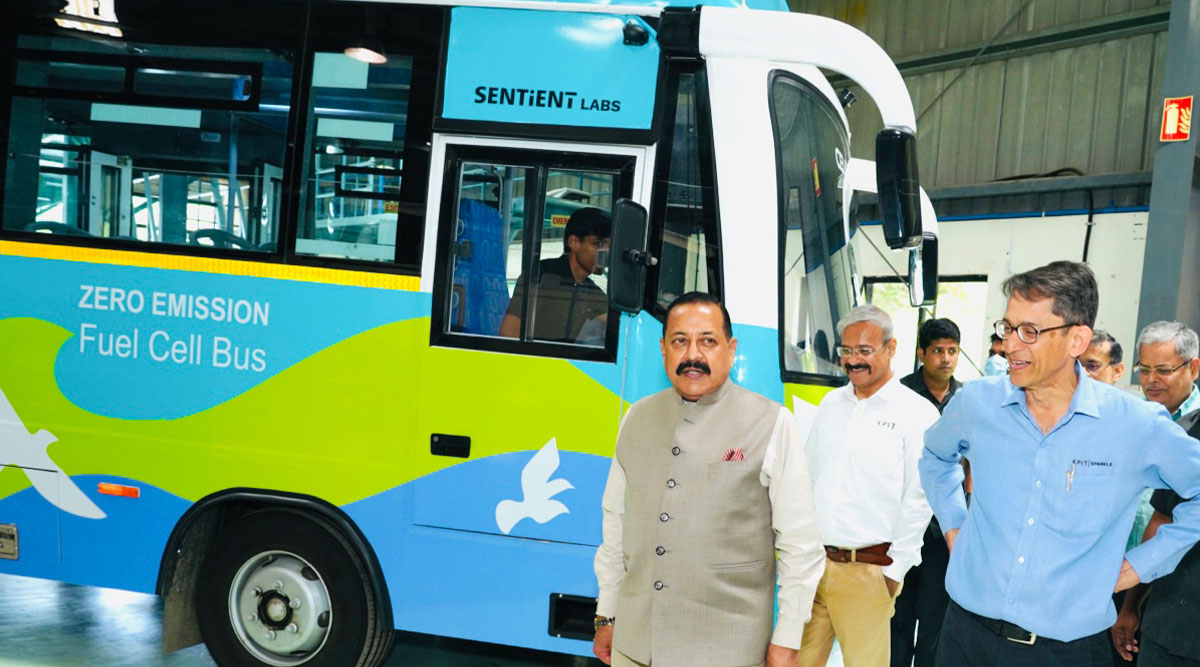
A hydrogen fuel cell bus developed by KPIT-CSIR in Pune was unveiled by Jitendra Singh, Union minister of state for Science and Technology, yesterday. The hydrogen fuel cell uses hydrogen and air to generate electricity, producing only heat and water in the process.
Hydrogen fuel cells like the one present in the bus produce electricity by combining hydrogen and oxygen atoms. The two gases react across an electrochemical cell similar to a conventional battery cell to produce electricity, water and small amounts of heat. This electricity is then used by electric motors to propel the vehicle forward.
What is a hydrogen fuel cell?
According to the US Department of Energy, fuel cells work in a similar manner to conventional batteries found in electric vehicles but they do not run out of charge and don’t need to be recharged with electricity. They continue to produce electricity as long as there is a supply of hydrogen. Just like conventional cells, a fuel cell consists of an anode (negative electrode) and cathode (positive electrode) sandwiched around an electrolyte.
Hydrogen is fed to the anode and air is fed to the cathode. At the anode, a catalyst separates the hydrogen molecules into protons and electrons and both subatomic particles take different paths to the cathode. The electrons go through an external circuit, creating a flow of electricity that can be used to power electric motors. The protons, on the other hand, move to the cathode through the electrolyte. Once there, they unite with oxygen and electrons to produce water and heat.
What is the advantage of a hydrogen fuel cell-powered vehicle?
The primary advantage of hydrogen fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEV) is that they produce no tailpipe emissions. They only emit water vapour and warm air. Another advantage is that they are more efficient than internal combustion engine vehicles.
Hydrogen fuel cell electric vehicles have another advantage when it comes to refuelling time, which makes them more practical than battery-powered electric vehicles for public transportation purposes. Even with the fastest charging technologies, it could take hours to charge a battery-powered electric bus. Meanwhile, hydrogen can be refilled in a fuel cell vehicle in a matter of minutes, nearly as fast as an internal combustion engine can be refilled with fossil fuels.
While this disadvantage may not be a major issue for battery-powered personal vehicles, for buses and other public vehicles, it could mean that an important asset is out of use for a large part of the day because it needs to be charged.
Are hydrogen fuel cell vehicles environmentally friendly?
One crucial point to note is that using a battery-powered electric vehicle doesn’t mean that the vehicles produce no emissions, but rather, that they produce no tailpipe emissions. Since a majority of the electricity in the country comes from fossil fuels, and the biggest source of hydrogen in the world currently is also fossil fuels, these vehicles do cause a large number of emissions with their usage.
But just like we are moving towards renewable sources of electricity, we could also move towards renewable methods of generating hydrogen in the future. So even if these vehicles do contribute to emissions right now, the fuel that they need could be produced using renewable methods such as solar and wind energy.
!function(f,b,e,v,n,t,s)
{if(f.fbq)return;n=f.fbq=function(){n.callMethod?
n.callMethod.apply(n,arguments):n.queue.push(arguments)};
if(!f._fbq)f._fbq=n;n.push=n;n.loaded=!0;n.version=’2.0′;
n.queue=[];t=b.createElement(e);t.async=!0;
t.src=v;s=b.getElementsByTagName(e)[0];
s.parentNode.insertBefore(t,s)}(window, document,’script’,
‘https://connect.facebook.net/en_US/fbevents.js’);
fbq(‘init’, ‘444470064056909’);
fbq(‘track’, ‘PageView’);